
| CV | Google Scholar | Github | LinkedIn | |
I am an PhD student at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign working with
Professor Alexander Schwing and Liangyan Gui.
My research interests include computer vision and machine learning. My goal is to build systems that can understand, infer, and recreate the visual world.
|

UIUC |

Meta |

Adobe |

Snap Inc. |

CMU |

Snap Inc. |

Microsoft |
|---|
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
Diffusion models have shown powerful image generation capability, yet 3D-aware image editing remains a challenging task, particularly when preserving the object content identity from a single image. To tackle this problem, we propose 3D-Fixup, a new framework for editing 2D images guided by learned 3D priors, which supports hard editing cases such as object translation and 3D rotation. We leverage a training-based approach that harnesses the genera- tive power of diffusion models, and turn to video data for generating training pairs, given that the video frames nat- urally encode real-world physical dynamics. Rather than relying solely on a single trained model to infer transforma- tions between source and target frames, we incorporate 3D guidance from an Image-to-3D model, which helps bridge this challenging task by explicitly projecting 2D information into 3D space. We design a data generation pipeline to ensure high-quality 3D guidance throughout training. Results show that by integrating these 3D priors, 3D-Fixup effec- tively supports complex, identity coherent 3D-aware edits, achieving high-quality results and advancing the applica- tion of diffusion models in realistic image manipulation.
@article{cheng20253dfixup,
title={{3D-Fixup: Advancing Photo Editing with 3D Priors}},
author={Cheng, Yen-Chi and Singh, Krishna Kumar and Yoon, Jae Shin and Schwing, Alex and Gui, Liangyan and Gadelha, Matheus and Guerrero, Paul and Zhao, Nanxuan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.10566},
year={2025}
}
|
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
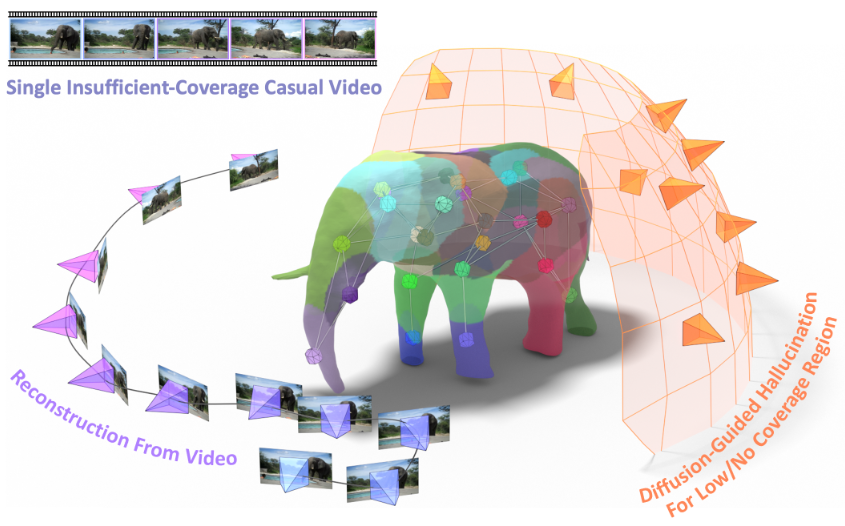
Articulated 3D reconstruction has valuable applications in various domains, yet it remains costly and demands intensive work from domain experts. Recent advancements in template-free learning methods show promising results with monocular videos. Nevertheless, these approaches necessitate a comprehensive coverage of all viewpoints of the subject in the input video, thus limiting their applicability to casually captured videos from online sources. In this work, we study articulated 3D shape reconstruction from a single and casually captured internet video, where the subject's view coverage is incomplete. We propose DreaMo that jointly performs shape reconstruction while solving the challenging low-coverage regions with view-conditioned diffusion prior and several tailored regularizations. In addition, we introduce a skeleton generation strategy to create human-interpretable skeletons from the learned neural bones and skinning weights. We conduct our study on a self-collected internet video collection characterized by incomplete view coverage. DreaMo shows promising quality in novel-view rendering, detailed articulated shape reconstruction, and skeleton generation. Extensive qualitative and quantitative studies validate the efficacy of each proposed component, and show existing methods are unable to solve correct geometry due to the incomplete view coverage.
@article{tu2023dreamo,
title={DreaMo: Articulated 3D Reconstruction From A Single Casual Video},
author={Tu, Tao and Li, Ming-Feng and Lin, Chieh Hubert and Cheng, Yen-Chi and Sun, Min and Yang, Ming-Hsuan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.02617},
year={2023}
}
|

|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code
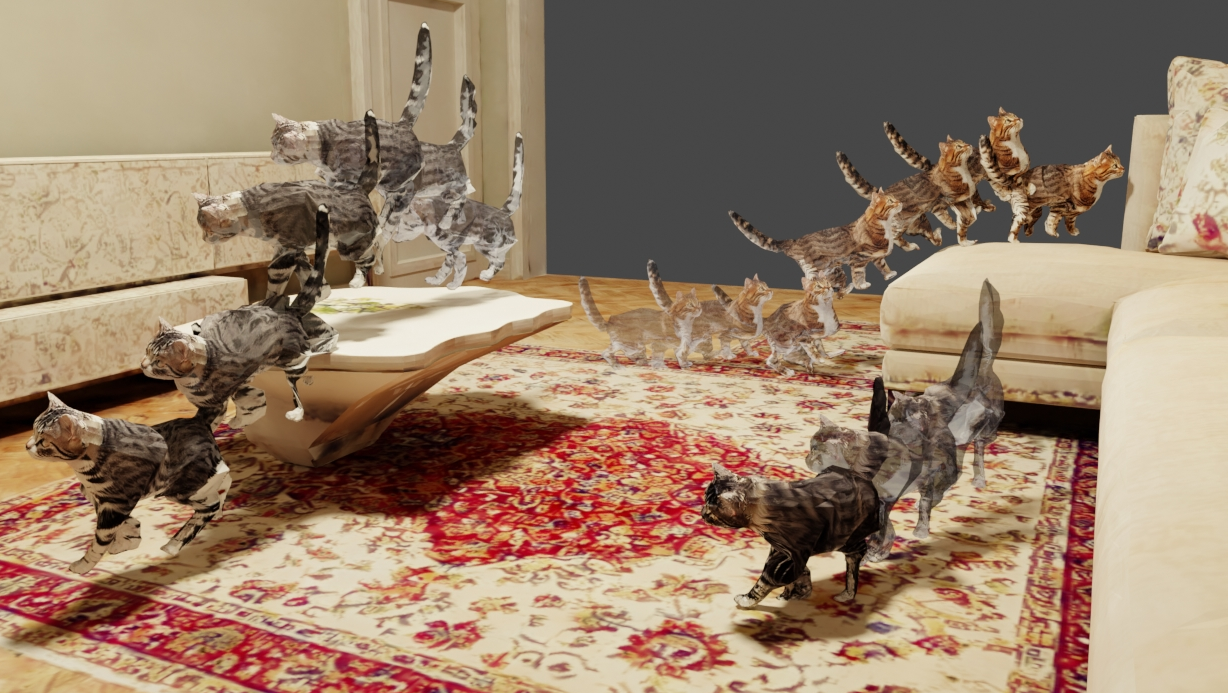
Toward unlocking the potential of generative models in immersive 4D experiences, we introduce Virtual Pet, a novel pipeline to model realistic and diverse motions for target animal species within a 3D environment. To circumvent the limited availability of 3D motion data aligned with environmental geometry, we leverage monocular internet videos and extract deformable NeRF representations for the foreground and static NeRF representations for the background. For this, we develop a reconstruction strategy, encompassing species-level shared template learning and per-video fine-tuning. Utilizing the reconstructed data, we then train a conditional 3D motion model to learn the trajectory and articulation of foreground animals in the context of 3D backgrounds. We showcase the efficacy of our pipeline with comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations using cat videos. We also demonstrate versatility across unseen cats and indoor environments, producing temporally coherent 4D outputs for enriched virtual experiences.
@article{cheng2023VirtualPets,
title={{V}irtual {P}ets: Animatable Animal Generation in 3D Scenes},
author={Cheng, Yen-Chi and Lin, Chieh Hubert and Wang, Chaoyang and Kant, Yash and Tulyakov, Sergey and Schwing, Alexander G and Gui, Liangyan and Lee, Hsin-Ying},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.14154},
year={2023},
}
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code
In this work, we present a novel framework built to simplify 3D asset generation for amateur users. To enable interactive generation, our method supports a variety of input modalities that can be easily provided by a human, including images, text, partially observed shapes and combinations of these, further allowing to adjust the strength of each input. At the core of our approach is an encoder-decoder, compressing 3D shapes into a compact latent representation, upon which a diffusion model is learned. To enable a variety of multi-modal inputs, we employ task-specific encoders with dropout followed by a cross-attention mechanism. Due to its flexibility, our model naturally supports a variety of tasks, outperforming prior works on shape completion, image-based 3D reconstruction, and text-to-3D. Most interestingly, our model can combine all these tasks into one swiss-army-knife tool, enabling the user to perform shape generation using incomplete shapes, images, and textual descriptions at the same time, providing the relative weights for each input and facilitating interactivity. Despite our approach being shape-only, we further show an efficient method to texture the generated shape using large-scale text-to-image models.
@article{cheng2023sdfusion,
title={{SDFusion}: Multimodal 3D Shape Completion, Reconstruction, and Generation},
author={Cheng, Yen-Chi and Lee, Hsin-Ying and Tulyakov, Sergey and Schwing, Alex and Gui, Liangyan},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2023}
}
|
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code
Powerful priors allow us to perform inference with insufficient information. In this paper, we propose an autoregressive prior for 3D shapes to solve multimodal 3D tasks such as shape completion, reconstruction, and generation. We model the distribution over 3D shapes as a non-sequential autoregressive distribution over a discretized, low-dimensional, symbolic grid-like latent representation of 3D shapes. We demonstrate that the proposed prior is able to represent distributions over 3D shape spaces conditioned over information from an arbitrary set of spatially anchored query locations. This enables us to represent distributions over 3D shapes conditioned on information from an arbitrary set of spatially anchored query locations and thus perform shape completion in such arbitrary settings (\eg generating a complete chair given only a view of the back leg). We also show that the learned autoregressive prior can be leveraged for conditional tasks such as single-view reconstruction and language-based generation. This is achieved by learning task-specific `naive' conditionals which can be approximated by light-weight models trained on minimal paired data. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method using both quantitative and qualitative evaluation and show that the proposed method outperforms the specialized state-of-the-art methods trained for individual tasks.
@inproceedings{autosdf2022,
author = {
Mittal, Paritosh and
Cheng, Yen-Chi and
Singh, Maneesh and
Tulsiani, Shubham
},
title = {{AutoSDF}: Shape Priors for 3D Completion, Reconstruction and Generation},
booktitle = {CVPR},
year = {2022}
}
|
|

|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code (coming soon)
Image outpainting seeks for a semantically consistent extension of the input image beyond its available content. Compared to inpainting -- filling in missing pixels in a way coherent with the neighboring pixels -- outpainting can be achieved in more diverse ways since the problem is less constrained by the surrounding pixels. Existing image outpainting methods pose the problem as a conditional image-to-image translation task, often generating repetitive structures and textures by replicating the content available in the input image. In this work, we formulate the problem from the perspective of inverting generative adversarial networks. Our generator renders micro-patches conditioned on their joint latent code as well as their individual positions in the image. To outpaint an image, we seek for multiple latent codes not only recovering available patches but also synthesizing diverse outpainting by patch-based generation. This leads to richer structure and content in the outpainted regions. Furthermore, our formulation allows for outpainting conditioned on the categorical input, thereby enabling flexible user controls. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the proposed method performs favorably against existing in- and outpainting methods, featuring higher visual quality and diversity.
@article{cheng2021inout,
author = {
Cheng, Yen-Chi and
Lin, Chieh Hubert and
Lee, Hsin-Ying and
Ren, Jian and
Tulyakov, Sergey and
Yang, Ming-Hsuan
},
title = {{In&Out}: Diverse Image Outpainting via GAN Inversion},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.00675},
year = {2021}
}
|

|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code (coming soon)
Image outpainting seeks for a semantically consistent extension of the input image beyond its available content. Compared to inpainting -- filling in missing pixels in a way coherent with the neighboring pixels -- outpainting can be achieved in more diverse ways since the problem is less constrained by the surrounding pixels. Existing image outpainting methods pose the problem as a conditional image-to-image translation task, often generating repetitive structures and textures by replicating the content available in the input image. In this work, we formulate the problem from the perspective of inverting generative adversarial networks. Our generator renders micro-patches conditioned on their joint latent code as well as their individual positions in the image. To outpaint an image, we seek for multiple latent codes not only recovering available patches but also synthesizing diverse outpainting by patch-based generation. This leads to richer structure and content in the outpainted regions. Furthermore, our formulation allows for outpainting conditioned on the categorical input, thereby enabling flexible user controls. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the proposed method performs favorably against existing in- and outpainting methods, featuring higher visual quality and diversity.
@article{lin2021infinity,
author = {
Lin, Chieh Hubert and
Le, Hsin-Ying and
Cheng, Yen-Chi and
Tulyakov, Sergey and
Yang, Ming-Hsuan
},
title = {{InfinityGAN}: Towards Infinite-Resolution Image Synthesis},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.03963},
year = {2021}
}
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code
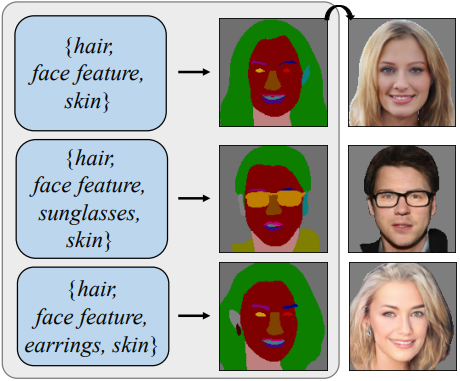
Flexible user controls are desirable for content creation and image editing. A semantic map is commonly used intermediate representation for conditional image generation. Compared to the operation on raw RGB pixels, the semantic map enables simpler user modification. In this work, we specifically target at generating semantic maps given a label-set consisting of desired categories. The proposed framework, SegVAE, synthesizes semantic maps in an iterative manner using conditional variational autoencoder. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that the proposed model can generate realistic and diverse semantic maps. We also apply an off-the-shelf image-to-image translation model to generate realistic RGB images to better understand the quality of the synthesized semantic maps. Furthermore, we showcase several real-world image-editing applications including object removal, object insertion, and object replacement.
@inproceedings{cheng2020segvae,
Author = {
Cheng, Yen-Chi and
Lee, Hsin-Ying and
Sun, Min and
Yang, Ming-Hsuan
},
Title = {Controllable Image Synthesis via {SegVAE}},
Booktitle = {ECCV},
Year = {2020}
}
|
|
webpage |
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv |
code
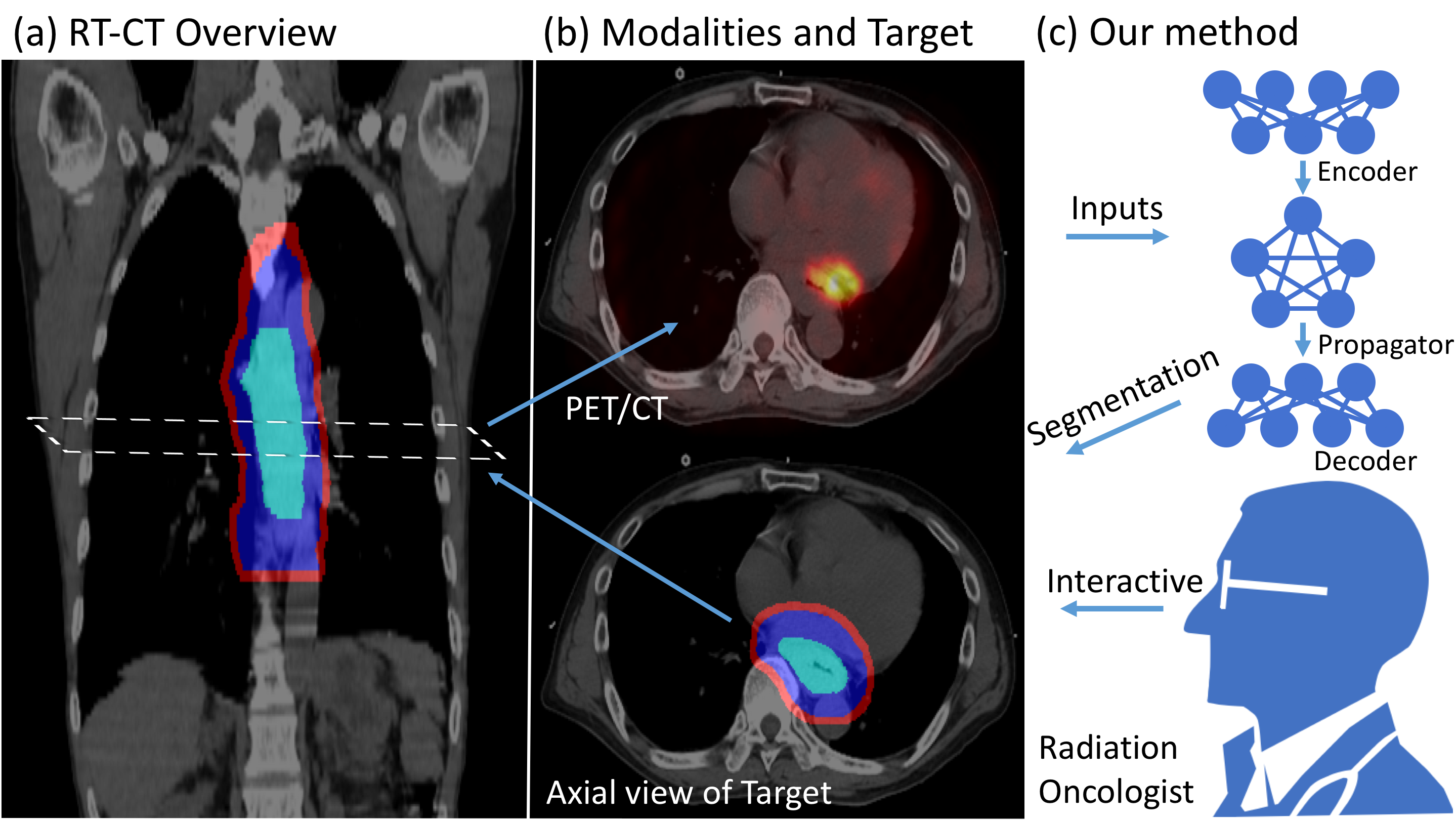
While image synthesis achieves tremendous breakthroughs (e.g., generating realistic faces), video generation is less explored and harder to control, which limits its applications in the real world. For instance, video editing requires temporal coherence across multiple clips and thus poses both start and end constraints within a video sequence. We introduce point-to-point video generation that controls the generation process with two control points: the targeted start- and end-frames. The task is challenging since the model not only generates a smooth transition of frames but also plans ahead to ensure that the generated end-frame conforms to the targeted end-frame for videos of various lengths. We propose to maximize the modified variational lower bound of conditional data likelihood under a skip-frame training strategy. Our model can generate end-frame-consistent sequences without loss of quality and diversity. We evaluate our method through extensive experiments on Stochastic Moving MNIST, Weizmann Action, Human3.6M, and BAIR Robot Pushing under a series of scenarios. The qualitative results showcase the effectiveness and merits of point-to-point generation.
@inproceedings{wang2019p2pvg,
Author = {Wang, Tsun-Hsuan and
Cheng, Yen-Chi and
Lin, Chieh Hubert and
Chen, Hwann-Tzong and
Sun, Min},
Title = {Point-to-Point Video Generation},
Booktitle = {ICCV},
Year = {2019}
}
|
|
abstract |
bibtex |
arXiv
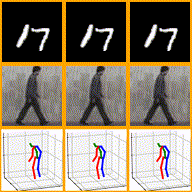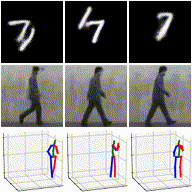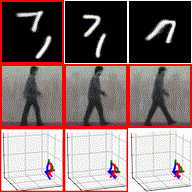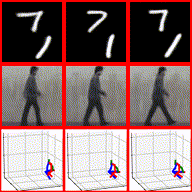
Tomography medical imaging is essential in the clinical workflow of modern cancer radiotherapy. Radiation oncologists identify cancerous tissues, applying delineation on treatment regions throughout all image slices. This kind of task is often formulated as a volumetric segmentation task by means of 3D convolutional networks with considerable computational cost. Instead, inspired by the treating methodology of considering meaningful information across slices, we used Gated Graph Neural Network to frame this problem more efficiently. More specifically, we propose convolutional recurrent Gated Graph Propagator (GGP) to propagate high-level information through image slices, with learnable adjacency weighted matrix. Furthermore, as physicians often investigate a few specific slices to refine their decision, we model this slice-wise interaction procedure to further improve our segmentation result. This can be set by editing any slice effortlessly as updating predictions of other slices using GGP. To evaluate our method, we collect an Esophageal Cancer Radiotherapy Target Treatment Contouring dataset of 81 patients which includes tomography images with radiotherapy target. On this dataset, our convolutional graph network produces state-of-the-art results and outperforms the baselines. With the addition of interactive setting, performance is improved even further. Our method has the potential to be easily applied to diverse kinds of medical tasks with volumetric images. Incorporating both the ability to make a feasible prediction and to consider the human interactive input, the proposed method is suitable for clinical scenarios.
@article{chao18radiotherapy,
title = {Radiotherapy Target Contouring with Convolutional Gated Graph Neural
Network},
author = {Chao, Chun-Hung and Cheng, Yen-Chi and Cheng, Hsien-Tzu and Huang, Chi-Wen and
Ho, Tsung-Ying and Tseng, Chen-Kan
Lu, Le and Sun, Min},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02912},
year = {2019},
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Template from this website. |